Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. Management can use this information to forecast budget estimates as well as predict future production schedules based on predicted sales. This blog explains types of variance, how to calculate it, & provides analysis examples. As a control technique, CVP analysis is used to measure the performance of the different departments in a company.
Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis and Contribution Margin
- CVP analysis shows the relationships among a business’s costs, volume, and profits.
- For example, if unit selling prices, unit variable costs, and total fixed costs remain constant, the P/V graph can show how many units must be sold to achieve a target profit.
- This will allow you to estimate how this affects the other variables involved, such as sales price or quantity produced.
- Plugging into your financial reports ensures this valuable data is updated in real-time.
To get the answer in dollars, divide fixed costs by the contribution margin ratio. The sales price is the amount of money that a company charges for its products or services. In Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) analysis, the sales price is an important component used to calculate contribution margin, break-even point, and profitability.
What are the Components of a Cost Volume Profit Chart?
Performing this type of analysis usually requires data from multiple sources and the involvement of multiple people. A tool like Layer allows you to seamlessly connect your data and automate data flows to update your calculations. Finally, you can calculate the margin of safety – in dollars or as a percentage of sales – to calculate how much sales could drop while still breaking even. In this article, you will learn about CVP analysis and its components, as well as the assumptions and limitations of this method. Additionally, you will learn how to carry out this type of analysis in Google Sheets, so you can easily repeat it periodically.
Cost Volume Profit Analysis
With its simple yet powerful visual representation, a cost volume profit chart provides valuable insights into a company’s financial performance. It allows you to analyze the relationship between costs, volume, and profit. This enables you to optimize your business’s operations and plan for the future.
Which activity is most important to you during retirement?
Using Layer, you can seamlessly connect your data across multiple locations and formats, and the whole team will have access to updated information. Ultimately, CVP analysis provides a clear picture of a business’s financial situation and allows for strategic planning to achieve long-term success. Thus ABC limited the need to sell units of electric fans to break even at the current cost structure. Aside from volume, other elements like inflation, efficiency, capacity and technology impact on costs.
What Does Cost Volume Profit (CVP) Chart Mean?
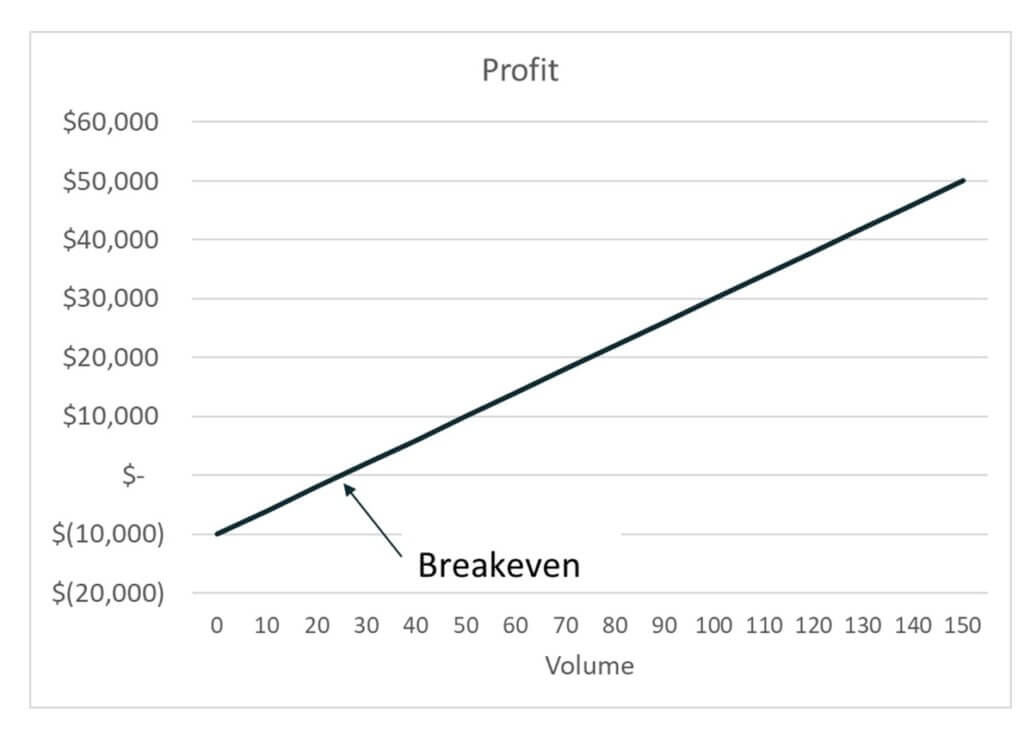
Semi-variable expenses must be split between expense classifications using the high-low method, scatter plot, or statistical regression. A cost-volume-profit (CVP) graph is a visual representation that illustrates the relationships between costs, sales volume, and profits in a business. This graph helps in understanding how changes in costs and volume affect a company’s operating income tax definition income and net income. By plotting total revenue and total costs on the same graph, businesses can easily identify the break-even point where total revenues equal total costs, which is essential for decision-making. In summary, the break-even point is the level of sales at which a company’s total revenues are equal to its total costs, resulting in neither a profit nor a loss.
It is that point at which volume of sales equals total expenses (both fixed and variable). Thus CVP analysis helps decision-makers understand the effect of a change in sales volume, price, and variable cost on the profit of an entity while taking fixed cost as unchangeable. Businesses can use the contribution margin to make informed decisions about pricing, product mix, and resource allocation. For example, the company could use the contribution margin to determine the profitability of a new product line or to analyze the impact of changes in selling prices or variable costs. By analyzing variable costs in CVP analysis, businesses can make informed decisions about pricing, product mix, and resource allocation.
The contribution margin income statement is usedquite frequently since it separates fixed and variable costs toallow a company to see what it can directly change and what itcannot change. This video will give you an example of the why andhow to do a contribution margin income statement. On the X-axis is “the level of activity” (for instance, the number of units). Notice how the area between the sales line and total cost line is red below the break-even and green above it. Managers can use this graph to predict the future losses if projected sales aren’t met.
The contribution margin per unit is calculated by subtracting the variable cost per unit from the selling price per unit. Cost volume profit analysis is a financial planning tool frequently used to assess the viability of short-term strategies. Among other things, break-even and what-if analyses are carried out for a variety of scenarios to estimate the effects on profits of short-term changes in cost, volume, and selling price. In summary, the sales price is an important component of Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) analysis. By understanding the impact of changes in sales price on contribution margin, break-even point, and profitability, businesses can make informed decisions about pricing that maximize profits. Variable costs are costs that vary with the level of production or sales.

